
Understanding PPP and PPP Authentication
PPP Components
The PPP Model
PPP Session Establishment
Phases
Link
Establishment Phase
Authentication
Phase (optional)
Password
Authentication Protocol
Challenge
Handshake Authentication Protocol
Network-layer
Protocol Phase
A Typical PPP
Session
The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) provides a method for
transmitting datagrams over serial point-to-point links. The PPP
Protocol, itself, is outlined in RFC 1661. There
are several other IETF Request For Comment (RFC) papers that
outline different aspects of PPP including PPP Authentication,
IP/AppleTalk/IPX over PPP and even the PPP Multilink Protocol.
PPP has three main components:
- A method for encapsulating datagrams over serial links.
- A Link Control Protocol (LCP) for establishing,
configuring, and testing the data-link connection.
- A family of Network Control Protocols (NCPs) for
establishing and configuring different network-layer
protocols.
In order to establish communications over a point-to-point
link, each end of the PPP link must first send LCP packets to
configure and test the data link. After the link has been
established and optional facilities have been negotiated as
needed by the LCP, PPP must send NCP packets to choose and
configure one or more network-layer protocols. Once each of the
chosen network-layer protocols has been configured, datagrams
from each network-layer protocol can be sent over the link.
The link will remain configured for
communications until explicit LCP or NCP packets close the link
down, or until some external event occurs (an inactivity timer
expires or network administrator intervention).
The PPP Model
| Table 1. |
Higher-Layer Protocols
|
| Network-Control Protocol (NCP) (specific
to each Network-Layer Protocol)
Examples are:
BCP - Bridge Control Protocol
IPCP - Internet Protocol Control Protocol
IPXCP - Internetwork Packet Exchange Control
Protocol
|
Link-Control Protocol (LCP)
|
High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC)
|
Physical Layer (such as EIA-232, V.24,
V.35)
|
|
PPP session establishment also has three phases:
- Link establishment phase - In this
phase, each Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) device sends
LCP packets to configure and test the data link. LCP
packets contain a Configuration Option field that allows
devices to negotiate on the use of options such as:
-
- Maximum Receive Unit (MRU)
- Compression of certain PPP fields
- Link authentication protocol
If a Configuration Option is not included in the LCP
packet, the default value for that Option is assumed.
- Authentication
phase (optional) - The peer may be authenticated
after the link has been established, using the
authentication protocol decided on. If authentication is
used, it must take place prior to starting the
network-layer protocol phase.
- PPP supports two authentication protocols:
- Password Authentication
Protocol (PAP)
PAP provides a simple method for a remote
node to establish its identity using a
two-way handshake. This is done only upon
initial link establishment.
After the PPP link establishment phase is
complete, a username/password pair is
repeatedly sent by the remote node across the
link until authentication is acknowledged, or
the the connection is terminated.
PAP is not a b authentication
protocol. Passwords are sent across the link
in clear text and there is no protection from
playback or trail-and-error attacks. The
remote node is in control of the frequency
and timing of the login attempts.
Here's an example of PPP Authentication
using PAP:
| Diagram 1. |
 |
- Challenge Handshake
Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
CHAP is used to periodically verify the
identity of the remote node using a 3-way
handshake. This is done upon initial link
establishment and can be repeated any time
after the link has been established.
After the PPP link establishment phase is
complete, the host sends a
"challenge" message to the remote
node. The remote node responds with a value
calculated using a one-way has function
(typically message-digest algorithm MD5). The
host checks the response against its own
calculation of the expected hash value. If
the values match, the authentication is
acknowledged. Otherwise, the connection is
terminated.
CHAP provides protection against playback
attack through the use of a variable
challenge value that is unique and
unpredictable. The use of repeated challenges
is intended to limit the time of exposure to
any single attack. The host (or a third-party
authentication server such as Terminal Access
Controller Access Control System - TACACS) is
in control of the frequency and timing of the
challenges.
Here's an example of PPP Authentication
using CHAP:
| Diagram 2. |
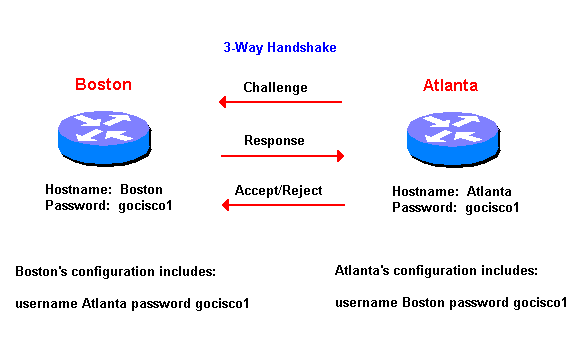 |
- Network-layer protocol phase - In
this phase, the PPP devices send NCP packets to choose
and configure one or more network layer protocols (such
as IP, IPX, and AppleTalk). Once each of the chosen
network-layer protocols has been configured, datagrams
from each network-layer protocol can be sent over the PPP
link.
The following is a diagram showing a typical PPP session.
| Diagram 3. |
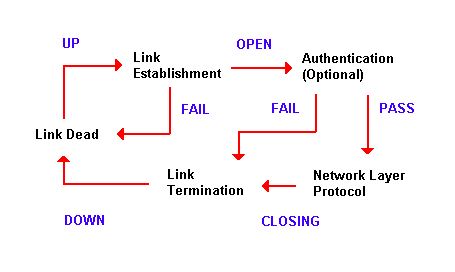 |
All contents copyright © 1992--1999 Cisco Systems, Inc. Important Notices and Privacy Statement.



